Irina Nesheva,
Olga Bozhkova
National Sports Academy “V. Levski”
https://doi.org/10.53656/str2025-2s-8-imp
Abstract. Health Wellness is an approach to health that encompasses maintaining and improving physical, mental, and emotional well-being through proactive, positive, and holistic wellness practices. Because of the relevance of this contemporary global issue, the research is committed to the creation and validation of a holistic wellness methodology targeting overweight students and working people. Based on the analysis of current research and applying a competency-based approach, the aim is to create a comprehensive Wellness Yoga training program in individual or group classes. This holistic wellness program aims to provide a positive effect and highlight its importance in applying an interdisciplinary principle that combines knowledge and methodologies from different fields. A positive effect was found at the end of the program on the persons studied.
Keywords: health wellness; yoga practice; training; interdisciplinary holistic approach
Introduction
The Global Wellness Institute defines wellness as the active pursuit of activities, choices, and lifestyles that lead to a state of holistic (whole) health1. Wellness is a state of happiness, health, or success that can be defined in one word as well-being or well-being2.
The evolution of the wellness concept is a complex and multi-layered process that traces the changing understandings of health and well-being over the centuries. From magical and religious practices to modern scientific approaches, wellness continues to evolve, responding to the needs and challenges of each era (Dimitrova 2016; Dimitrova 2019).
Wellness is an approach to health that encompasses the maintenance and improvement of physical, mental, and emotional well-being through proactive, positive, and holistic wellness practices.
The genesis of the wellness concept is seen as the result of the symbiosis and evolution of science and human culture refracted through the prism of the new millennium. It is accepted that the transition from achieving a purely therapeutic effect to the purposeful creation of well-being, comfort, and care for the health of the individual continues its evolutionary development, to reach the modern form of understanding the wellness concept, the basis of which is “Health Promotion and Disease Prevention” (Vassileva 2012), and authors in their work consider health wellness in a multi-component way (Dimitrova et al. 2023).
Dr. Roger Smith adopts the following definition “Wellness is a conscious, purposeful and responsible approach that modifies an individual’s lifestyle to optimize personal health and achieve well-being, understood as a multidimensional dimension that includes physical, emotional, intellectual, social and spiritual health. To achieve this, various conventional and holistic practices, techniques, and teachings are applied that have an impact on the physical, emotional, intellectual, spiritual, social, and occupational spheres of an individual’s life“ (Davchev 2017).
Ivkov (2012) justifies that “Promotion of personal health, is an organized effort of professionals and society to educate the individual on issues of personal health and the development of a social system that provides each person with a standard of living adequate to maintain and improve health”.
Statement of the problem
The stress-adaptive response of humans is something necessary for survival and coping with life’s difficulties, but prolonged stress leads to chronically elevated cortisol levels. As a consequence, a rapid depletion of glucose stores occurs, which serves as a signal for the body to quickly replenish them. Cortisol causes an increase in appetite and a desire to immediately and in larger quantities the body to accept food, mostly sweet and fatty. On the other hand, it promotes the accumulation of fat in the cells with consequent obesity, reduces muscle mass, impedes the functioning of memory, and hence accompanying health problems. For a general adaptation syndrome and the effect of cortisol under stress, one of the pioneers on this topic Hans Celier (2018), which stress nowadays, is the number one enemy for people and its consequences – rapid weight gain.
It has been found that there is a link between emotional stress and obesity. Stress contributes to weight gain and the development of obesity according to the authors (Derya 2023; Dimitrova 2020) who recommend educational interventions among youth (presentations, lecture courses, and discussions).
Naturopathy is focused on the body’s ability to heal itself through diet and lifestyle changes, herbs, massage, and wellness practices for healthy aging (Tomova & Angelov 2023).
In this regard, the author (Ilinova 2014) argues that various sports and physical activities “increase a girl’s/woman’s physical fitness and strength potentially increasing individual attractiveness to the opposite sex, increasing self-esteem and sense of one’s attractiveness, so sport is also essential” not only for the female reproductive system but also for increasing the Wellbeing Index.
Body mass index (BMI) is a medical and biological indicator that is used to determine normal, healthy weight in people of different heights and serves to diagnose obesity or malnutrition. To determine the limits of overweight and obesity, the so-called body mass index (BMI), also known as the Quetelet index, is most commonly used. The following formula is used:
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)²
Women with body fat > 30% and men with body fat > 25% are defined as obese. In children and adolescents, the amount of adipose tissue changes with age, according to WHO (World Health Organization)3 criteria.
Methodology
In view of the relevance of the contemporary global problem, the research is devoted to the creation and validation of a wellness holistic methodology aimed at overweight students and working people.
According to Dimitrova (2016, 2023), different methodologies are used globally to measure healthy recreational exercise practices to achieve a healthy lifestyle according to Eastern or national traditions and culture as long as they are effective. Health-enhancing physical activities have a wide range of impacts when applied comprehensively.
The study focused on the application of an Eastern practice (yoga) that is a convenient and effective method of exercise not only for weight loss but also for improving the components of physical fitness, leading to a reduction in the health risk factors of overweight people and the process of obesity. In recent decades, yoga asanas (exercises) have become an alternative and beneficial program with a rehabilitative nature for fitness concerning people who have physical difficulties or obesity (Yogananda 1998).
Developing a holistic wellness methodology to reduce weight and increase the Wellness Index through yoga asana, breathing and meditation practices, diet, and outdoor nature hikes can impact emotional stress reduction and can have a significant positive effect on the overall health of individuals with elevated body mass index (Eknoyan 2008).
The study aimed to develop a model of a specialized holistic yoga methodology to reduce weight in overweight people and increase their global happiness index. The task we set ourselves was to establish the level of obesity (BMI) and the difference in individual weight of the participants at the beginning and at the end of the experiment.
The study group consisted of 30 persons aged (18±34) years. As applied yoga methodology was conducted 2 times in natural conditions (yoga studio) and 3 times in online home conditions.
In this context, the present study aims to analyze a group of individuals’ body mass, BMI-s, and the effect of hatha yoga practice (5p per week) combined with meditative stress control techniques and a nutritional weekly regimen. The research paper proposes an original Wellness Holistic Model for obesity presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Wellness holistic weekly program for overweight people (by Olga Bozhkova – Master in SPA Culture)

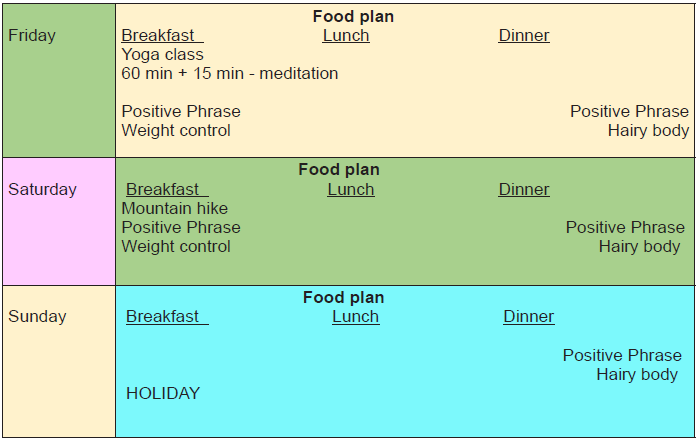
Data and analysis of results
The changes in body mass composition indices under the influence of the holistic yoga methodology and the integrated application of the eastern movement practice with the additional approaches described in Table 1 can be considered positive when the % TM was reduced within the short period of three months of the conducted experiment.
Before the implementation of the Holistic Wellness Methodology, participants in the study group were tested on two indicators of body mass index and participant weight, and after its three-month implementation. The results obtained were processed using analysis of variance on the variable of body mass index (BMI) presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Mean levels of variability Wilcoxon t-criterion
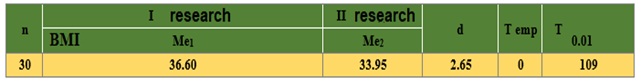
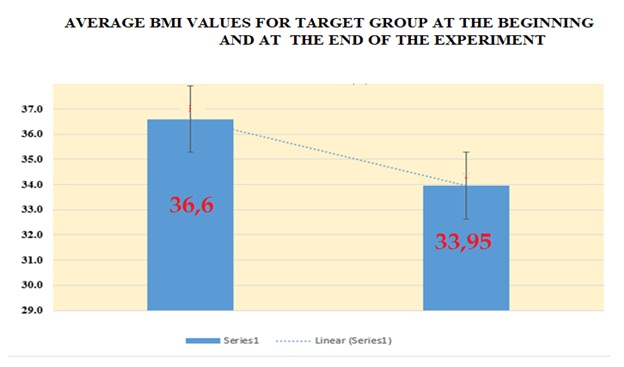
Figure 1. Mean BMI values at the beginning and the end of the experiment
Table 2 reveals the average levels of body mass index (BMI), at the beginning of the measurement period it was 36.6%, the total for all study subjects, after its completion the BMI decreased by 2.65% – 33.95%. Although, at first glance, the profit is not large for the short study period there is a significant progress of the study group. The difference is statistically significant.
A visualization of individual baseline and endpoint BMI data for the entire study group is presented in Figure 2.
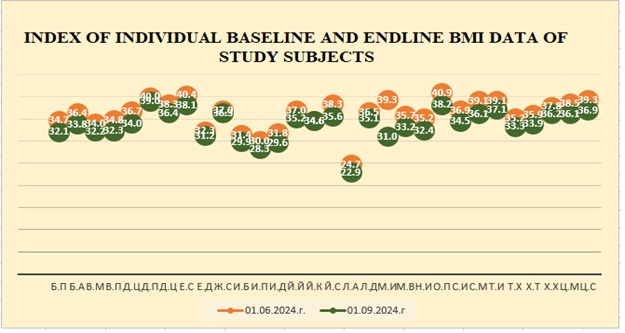
Figure 2. Individual BMI values – start and end date
Figure 2 shows that almost all participants made significant progress following the holistic methodology. The greatest difference was observed in the subject with initials M.I (М.И) where the body mass index of 39.3% had not decreased to 31%, with a difference of 8.3%, which is an exceptional achievement of any of the subjects in the short period.
Table 3 presents the mean levels of variability according to the Student’s t-criterion for dependent excerpts by weight indicator (kg).
Table 3. Descriptive statistics for weight indicator
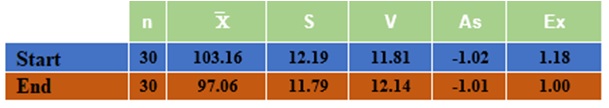
The mean values of the indicator – weight are presented, at the beginning of the study period the average weight was 103.16 kg, at the end of the experiment it decreased by 6.1 kg in total for the target group – 97.06 kg. Standard deviation and coefficient of variation, asymmetry, and excess are presented and presented graphically in Figure 3.
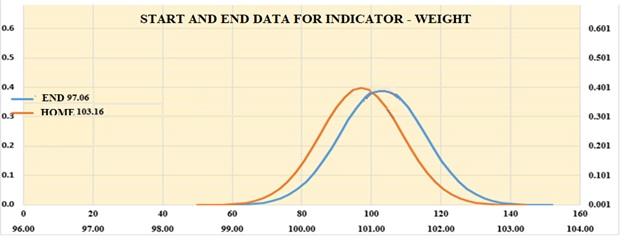
Figure 3. Graphical representation of the average values of the weight indicator at the beginning and end of the study
The biggest difference in measured weight was observed in S.M (С.М) who had reduced his body weight by 9 kg at the end of the experiment. Significant progress was also observed in two other subjects S.I (С.И) had reduced his weight by 8 kg and J.S (Й.С) where a weight reduction of 7.4 kg was observed after the, end of the holistic methodology. The individual values obtained are due to the more rapid metabolic process, being 20±22 years of age.
In conclusion
The results of the experiment show a very good impact on the subjects for the short period of three months in terms of BMI, weight index, and indices of mental well-being and balance, which will be presented in another paper.
With a focus on evidence-based practices, the Wellness methodology for health, weight loss, overall benefits, and mental well-being is an invaluable resource for individuals who wish to improve their health status and wellness by implementing meditation techniques and stress management exercises.
Holistic methodology is critical in educating and motivating individuals to prioritize their health and psycho-emotional well-being.
Acknowledgements and Funding
Project for the construction of a Centre of Excellence “Heritage BG”, funded by the Operational Programme “Science and Education for Smart Growth” and the Programme “Education: BG16RFPR002-1.014”.
NOTES
- https://globalwellnessinstitute.org/what-is-wellness/
- https://www.wellbeing.iastate.edu/wellbeing-blog/2015/11/wait-minuteis-it-wellbeing-or-well-being
- Health Conference, New York, 19-22 June – https://www.who.int/about/governance/constitution
REFERENCES
ANGELCHEVA, M., 2023. Complex SPA program effect on overweight women’s physical condition and Well-being. Trakia Journal of Sciences, vol. 21, Suppl. 3, 2023 (Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg), ISSN 1313-3551.
EKNOYAN, G., 2008. Adolphe Quetelet (1796 – 1874) – the average man and indices of obesity. Nephrol Dial Transplant. Jan; vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 47 – 51. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm517. Epub 2007 Sep 22.PMID: 17890752.
VASILEVA, M., 2012. Kontseptualna ramka na Spa i Uelnes turizma v Bulgaria, Disertatsia, p. 6 [In Bulgarian].
DAVCHEV, A., 2017. Development of the wellness concept in historical aspect and its effects in contemporary economy. UARD Yearbook, vol 5.
DERYA, E., 2023. Relationship between healthy life awareness, emotional eating, obesity awareness, and coping stress in adolescents. Psychology in the Schools, research article, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 1898 – 1917, https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22834.
DIMITROVA, B., 2016. Research impact through the scientific publications in Wellness culture. Monografia. Sofia. Izd. Avangard Prima. ISBN – 978-619-160-666-5.
DIMITROVA, B., 2019. Quality assessment about standards for wellness services and certified skills of specialized staff. Trakia Journal of Sciences, vol. 17, no. 2, рp.143 – 149. DOI: 10.15547 / tjs.2019.02.007. ISSN: 1313-3551 (online) / http://tru.uni-sz.bg/tsj/Vol.17 http://tru.uni-sz.bg/tsj/Vol.17,%20Suppl.2,%202019/7.pdf (Accessed 11 Oct 2024).
DIMITROVA, B., 2020. Relationships between education and innovations in the recreational Industry in Bulgaria. Trakia Journal of Sciences, vol. 3, pp. 194 – 202. DOI:10.15547/tjs.2020.03.003. ISSN: 1313-3551 (online), (uni-sz.bg) / http://tru.uni-sz.bg/tsj/Volume%2018,%202020,%20Number%203,%20Series%20Social%20Sciences/B.Dimitrova.pdf (Accessed 13 Oct 2024).
DIMITROVA, B., 2023. Ikonomichesko vazdeystvie na iztichaneto na mozatsi varhu razvitieto na uelnes i spa turizma v Bulgaria. Trakia Journal of Sciences, vol. 21, Suppl. 3. http://www.uni-sz.bg), ISSN 1313-35511 [In Bulgarian].
DIMITROVA, B.; ALEKSANDROVA, V.; NESHEVA, I. et al. 2023. Uelnes kultura, indeksi, destinatsii i uslugi. Sofia: Izd. NSA Pres, parvo izdanie [In Bulgarian], ISBN: 978-954-718-731-3.
TAN, S.Y.; YIP, A., 2018. Hans Selye (1907-1982): Founder of the stress theory. Singapore Med J. vol. 59, no. 4, pp. 170 – 171. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2018043. PMID: 29748693; PMCID: PMC5915631.
ILINOVA, B., 2014. Zhenata i sporta. Sofia: Avangard Prima. ISBN 978-619-160-381-7 [In Bulgarian].
IVKOV, B., 2012. Promotsia na zdraveto – osnovni ponyatia i definitsii, http://bojidarivkov.wordpress.com//11/01/ [In Bulgarian].
SMITH, R., 2017. The Believe in Wellness concept, Michigan University, art., p. 2, ISSN 1314-9113 (print), ISSN 2535-0609.
TOMOVA, T., ANGELOV, B., 2023. Wellness practices for healthy aging. Trakia Journal of Sciences, vol. 21, Suppl. 3 (Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg), ISSN 1313-3551.
YOGANANDA, P., 1998. Avtobiografia na edin yogin. Izd. Lik. ISBN 954-607-171-4 [In Bulgarian].
Dr. Irina Petkova–Nesheva, Assoc. Prof.
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-0436-6398
Olga Bozhkova
Department of Gymnastics
National Sports Academy “Vasil Levski”
E-mail: iranesheva2005@abv.bg
>> Download the article as a PDF file <<



